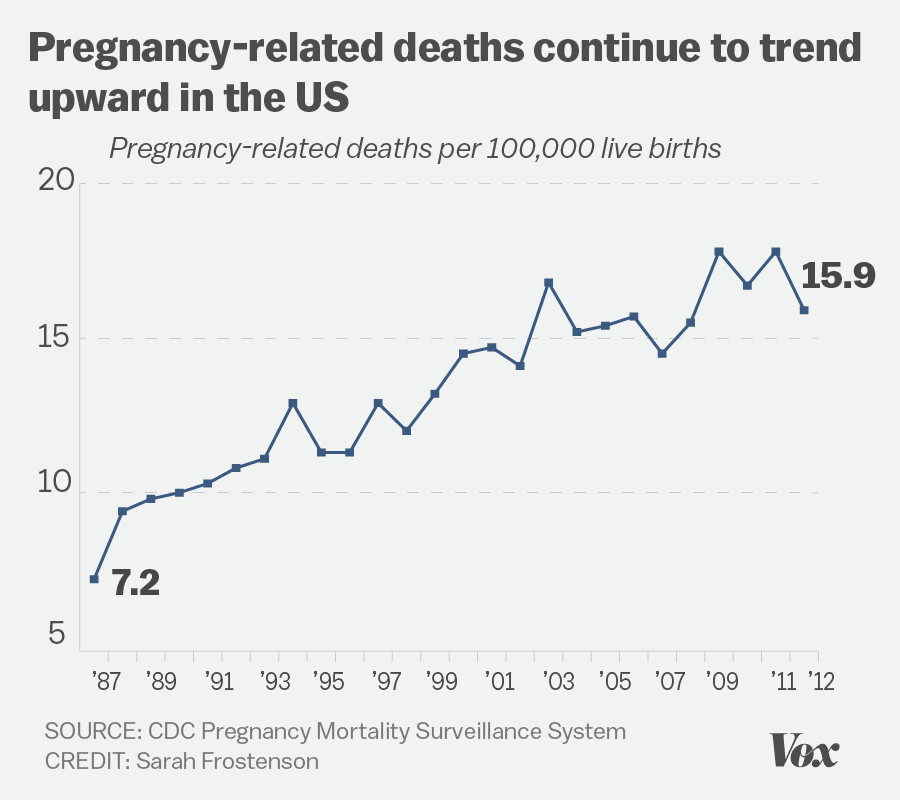
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths are on the rise, presenting a growing public health crisis that demands immediate attention. Alarmingly, the United States leads its high-income peers in maternal mortality rates, with over 80% of these deaths deemed preventable. Studies indicate that between 2018 and 2022, the rate of pregnancy-related mortality, driven by factors such as healthcare disparities and chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease, has only increased, particularly among marginalized racial groups. Comprehensive prenatal care and postpartum support are essential to mitigating these alarming trends; however, significant gaps remain in the U.S. healthcare system. As we delve deeper into this issue, it is crucial to explore the multifaceted aspects of maternal health, including the need for policy changes and enhanced postpartum care.
The alarming trend of increasing fatalities during and after pregnancy in the U.S. can be examined from several perspectives, including maternal health disparities, the lack of integrated care, and the impact of chronic medical conditions. Maternal death, a critical marker of healthcare quality, reflects broader systemic issues, including inequities experienced by women of color and those living in underserved areas. Furthermore, risk factors such as cardiovascular complications during pregnancy are contributing to this public health crisis. Given the heightened prevalence of severe postpartum complications, such as delayed effects of pregnancy on overall health, understanding and addressing these challenges is vital for improving outcomes. It is clear that urgent reforms are needed to ensure every mother has access to quality healthcare throughout their reproductive journey.
Understanding U.S. Pregnancy-Related Deaths
In recent years, U.S. pregnancy-related deaths have remained a concerning health issue, with statistics highlighting a troubling trend. In a country that prides itself on advanced medical care, the maternal mortality rate is alarmingly high compared to other developed nations. Between 2018 and 2022, the rate increased from 25.3 deaths per 100,000 live births to 32.6, reflecting a broader systemic problem within the healthcare infrastructure. Researchers attribute much of this crisis to the complexities of the U.S. healthcare system, which is fraught with disparities that primarily affect marginalized populations.
A significant portion of these deaths is preventable, with over 80% identified as manageable through proper prenatal care and attention to postpartum complications. Unfortunately, these preventive measures are often inaccessible to many women due to inequitable healthcare policies and regional disparities in the availability of maternity care. The focus must shift toward creating inclusive, supportive healthcare environments that prioritize the health of pregnant women from prenatal stages through childbirth and into postpartum care.
The Role of Healthcare Disparities in Maternal Mortality
Healthcare disparities represent a critical barrier to addressing maternal mortality rates in the U.S. Studies show that American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest pregnancy-related mortality rates, a staggering statistic compared to their white counterparts. This inequity raises significant concerns about the systemic biases embedded in the healthcare system, which can impact access to quality care. Addressing these disparities requires a multifaceted approach, integrating policies that foster equity and inclusivity in healthcare access across all racial and ethnic groups.
Furthermore, by actively acknowledging and confronting these disparities, healthcare providers can work towards developing targeted interventions that meet the needs of underserved populations. For example, improving access to culturally competent care and tailored health education programs can substantially reduce mortality rates among high-risk groups. Such initiatives not only focus on immediate medical needs but also encompass long-term health education and community support, ultimately fostering healthier pregnancy outcomes.
The Importance of Postpartum Care in Maternal Health
Postpartum care is an essential aspect of maternal health that has often been overlooked in broader discussions about maternal mortality. Recent data indicate that nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths occur during the late maternal period, which includes the timeframe up to one year postpartum. This underscores the need for comprehensive support systems that extend beyond the traditional six-week postpartum check-up, allowing healthcare providers to monitor and manage women’s health during this critical period.
A continuous approach to postpartum care ensures that new mothers receive the necessary support to recover from childbirth, thus addressing complications that may arise, such as cardiovascular disease and mental health disorders. By implementing structured postpartum care programs that focus on physical and mental wellness, we can greatly diminish the risk of late maternal deaths and enhance the overall health of mothers as they transition into parenthood.
Maternal Mortality and Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as a leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., accounting for approximately 20% of such fatalities. Hypertension, eclampsia, and other cardiovascular issues are increasingly manifesting in younger women, contributing significantly to rising mortality rates during and after pregnancy. As the demographics of pregnancy health evolve, healthcare providers must prioritize identifying and managing cardiovascular risk factors early in pregnancy to mitigate potential long-term repercussions.
Addressing cardiovascular conditions during pregnancy involves comprehensive screening and education on heart health, which can empower women to make informed decisions about their lifestyle and healthcare. Increased awareness among healthcare practitioners about the signs and symptoms of cardiovascular complications can lead to timely interventions, ultimately improving outcomes for both mothers and their children.
The Impact of COVID-19 on Maternal Health
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted maternal health across the U.S., exacerbating existing healthcare disparities and leading to a marked increase in pregnancy-related mortality rates. The ensuing health crisis not only strained healthcare resources but also altered how care was delivered, with many women facing barriers to accessing essential prenatal and postpartum services. Compounding these challenges were heightened levels of stress and anxiety among pregnant individuals, which could potentially influence health outcomes.
Moreover, the onset of the pandemic coincided with a documented increase in maternal deaths in 2021, reflecting the complex relationship between public health emergencies and reproductive healthcare. This situation calls for more robust public health policies to ensure that maternal health remains a priority even during crises, safeguarding access to care and support for pregnant women.
Innovative Solutions for Improving Maternal Outcomes
To combat the rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths, innovative solutions aimed at improving maternal care are essential. Initiatives must prioritize investing in public health infrastructure that offers comprehensive support throughout the pregnancy continuum, including prenatal, delivery, and postpartum care. Programs that implement community-based interventions to address specific needs within high-risk populations can significantly enhance the quality of care and reduce mortality.
Strengthening collaborations between healthcare providers, public health officials, and community organizations can also create more cohesive support networks for expecting and new mothers. Through such partnerships, information sharing and resource allocation can be optimized, ultimately creating a more equitable healthcare landscape leading to better maternal health outcomes.
Addressing Policy Differences Across States
One of the key findings from recent maternal health studies is the stark variation in pregnancy-related death rates across different states. This variation often reflects the inconsistencies in healthcare policies, access to quality care, and the availability of services for pregnant individuals. States like California demonstrate that with the right policies in place, it is possible to significantly reduce maternal mortality rates, indicating that systematic changes are paramount in areas experiencing higher death rates.
To address these disparities, targeted state-level policies need to be developed and implemented, focusing on resource allocation, workforce training, and amplifying public health campaigns that target maternal health. By learning from states that excel in maternal health outcomes, other regions can adopt best practices and strategies, creating a more uniform standard of care across the country.
Research Gaps in Maternal Health Statistics
Despite the advancements in tracking maternal health, significant gaps remain in our understanding of maternal mortality causes and rates. The lack of a consistent national system for monitoring maternal deaths until recently hindered accurate data collection and analysis. Without reliable data, developing effective policies and interventions to address maternal health challenges becomes increasingly difficult.
Moving forward, it is crucial for states to implement standardized tracking systems that capture not only pregnancy-related deaths but also the circumstances surrounding them. This data can inform healthcare strategies and illuminate where disparities exist, enabling targeted interventions that can lead to improvements in maternal health outcomes.
Investing in Public Health Infrastructure
Investment in public health infrastructure is vital to curbing the rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. As healthcare systems face budget cuts and resource constraints, a re-evaluation of funding priorities is needed to ensure that maternal health remains a focus of public health initiatives. Effective investments should include bolstering prenatal care services, improving postpartum support, and enhancing educational resources for healthcare providers to better serve pregnant women.
Additionally, supporting research initiatives that explore the underlying factors contributing to maternal mortality can lead to innovative solutions. By prioritizing maternal health as a critical public health issue, we can develop comprehensive strategies that not only address but also prevent pregnancy-related deaths.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths are primarily caused by cardiovascular diseases, which account for over 20% of these deaths. Other significant causes include hemorrhage, infections, and complications from conditions such as pre-eclampsia. Addressing these causes requires improved healthcare that focuses on both prenatal and postpartum care.
How do healthcare disparities contribute to U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
Healthcare disparities significantly contribute to U.S. pregnancy-related deaths by creating unequal access to quality maternal healthcare. Racial and ethnic groups, particularly American Indian and Alaska Native women, experience much higher maternal mortality rates due to systemic biases, inadequate access to care in maternity deserts, and lack of targeted health policies.
What role does postpartum care play in reducing U.S. maternal mortality?
Postpartum care is crucial in reducing U.S. maternal mortality as nearly one-third of pregnancy-related deaths occur between 42 days and one year after childbirth. Enhancing postpartum care infrastructure to support women during this period can help prevent complications and address chronic health conditions that may flare up after giving birth.
Why is cardiovascular disease a major concern for pregnancy health in the U.S.?
Cardiovascular disease has become a leading concern for pregnancy health in the U.S. due to increasing rates of chronic conditions like hypertension among younger women. Effective management of these issues during pregnancy is essential, as they can lead to serious complications and contribute significantly to the maternal mortality rate.
How can the U.S. improve its maternal health outcomes compared to other high-income countries?
The U.S. can improve maternal health outcomes by investing in public health infrastructure, implementing comprehensive policies to address healthcare disparities, and ensuring that quality prenatal and postpartum care is accessible to all women. Learning from states with better outcomes, like California, can provide a roadmap for nationwide improvements in maternal health.
What impact did the COVID-19 pandemic have on U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
The COVID-19 pandemic likely exacerbated U.S. pregnancy-related deaths, with a sharp increase in mortality rates observed in 2021. The pandemic has highlighted existing healthcare system gaps, making it critical to enhance support and resources for pregnant individuals, particularly during public health crises.
What measures can be taken to track U.S. pregnancy-related deaths effectively?
To track U.S. pregnancy-related deaths effectively, it’s essential to maintain a national surveillance system like the pregnancy checkbox on death certificates implemented in 2018. Continuous collection and analysis of comprehensive data will help identify trends, address disparities, and inform health policies to improve maternal outcomes.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Preventability | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable. |
| Maternal Mortality Rate | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, rising from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births from 2018 to 2022. |
| Racial Disparities | American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest rates at 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births, nearly four times that of white women. |
| Leading Cause of Death | Cardiovascular disease is now the leading cause, accounting for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Nearly one-third of pregnancy-related deaths occur between 42 days and one year postpartum, highlighting the need for better postpartum care. |
| Need for Improved Care | Investing in public health and innovative solutions for extended postpartum care is crucial for reducing rates. |
Summary
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths have been a serious issue, with preventable fatalities making up a significant portion of these tragedies. This concerning trend highlights systemic issues within the U.S. healthcare system, including disparities among racial groups and inadequate postpartum care. To reverse the rising trend in maternal mortality, it is imperative to invest in equitable healthcare solutions that focus on improving prenatal care and extending support for new mothers beyond the immediate postpartum period. Addressing the root causes of these preventable deaths will be essential for ensuring the health and safety of mothers across the United States.