Suicide prevention for older adults is an urgent public health priority, especially given that individuals aged 75 and above face the highest risk of suicide across any demographic. Despite this alarming trend, there is a significant lack of mental health resources for seniors tailored specifically to their needs. Recent studies reveal that awareness around elderly suicide remains critical, yet many platforms and initiatives often overlook this vulnerable population. It is crucial to address depression in elderly communities by enhancing the availability of online resources for older adults and promoting geriatric suicide prevention efforts. Raising awareness and providing accessible mental health support can make a profound difference in the lives of older adults as we strive to reduce the stigma and barriers surrounding suicide prevention among seniors.
Addressing the challenge of reducing suicidal tendencies in the senior population involves recognizing the unique factors affecting their well-being. Older adults often experience feelings of isolation and despair, contributing to mental health struggles that can lead to suicidal thoughts. With a growing concern for older individuals experiencing depression, it becomes vital to enhance available support systems and outreach programs designed specifically for the elderly. By fostering a comprehensive understanding of the mental health landscape for seniors, we can create targeted initiatives that prioritize their safety and emotional health. Efforts aimed at suicide prevention for this age group must emphasize the availability of tailored resources and the importance of community engagement to combat loneliness and hopelessness.
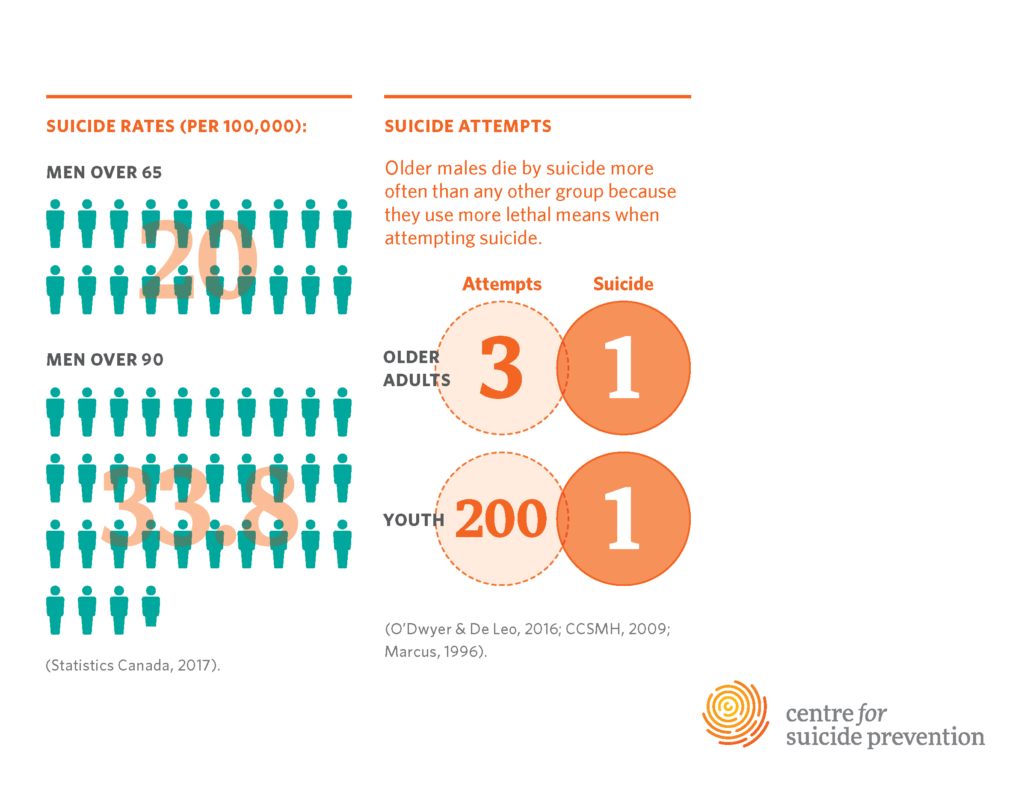
Understanding the High Suicide Rates Among Older Adults
Suicide rates have been rising among older adults, particularly those over the age of 75, who are now the demographic with the highest suicide rates according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. This troubling trend is attributed to various factors, including social isolation, health issues, and underrepresentation in mental health research. As this age group often encounters loneliness and a lack of social connections, the urgency to address their mental health needs is paramount.
Moreover, the increasing reliance of older adults on digital platforms to seek mental health resources is both a challenge and an opportunity. While leveraging online resources can assist in connecting them with support, the substantial gaps in available information and accessibility of suicide prevention resources exacerbate the issue. Establishing comprehensive strategies that target this demographic can help mitigate their elevated risks.
The Need for Tailored Suicide Prevention Resources
Despite the alarming statistics surrounding elderly suicide, many national suicide prevention organizations fall short in providing targeted resources for older adults. A recent study highlighted this disparity, showing that online resources geared towards elderly individuals are often scarce, buried under more widely recognized campaigns focused on younger populations. This oversight not only limits access to crucial information but also undermines the specific needs of older adults facing suicidal thoughts.
To rectify this imbalance, there is a pressing need for tailored mental health resources for seniors that focus on their unique circumstances. Campaigns must emphasize elderly suicide awareness, addressing factors such as physical health, mental well-being, and the socio-economic challenges that contribute to despair in later life. By creating content that resonates with older adults, organizations can foster a safer environment that encourages this population to seek help.
Exploring Geriatric Suicide Prevention Strategies
Geriatric suicide prevention efforts must encompass a multi-faceted approach that considers the complexities of aging. Effective strategies can include widespread community awareness initiatives, outreach programs targeting social isolation, and training for healthcare providers within geriatric psychiatry. By recognizing the nuances of mental health challenges specific to older adults, targeted interventions can be developed to support their unique needs.
Additionally, collaboration between mental health professionals and community organizations can enhance the reach of these initiatives. When tailored prevention programming is made available through established community channels and online resources for older adults, it not only raises awareness but also creates a supportive network that can significantly reduce the incidence of suicides in this vulnerable group.
Addressing Depression in Elderly Communities
Depression is a common yet often overlooked mental health issue among older adults, contributing to the high rates of suicide in this demographic. Symptoms of depression can manifest differently in older individuals, frequently leading to misdiagnosis or inadequate treatment. Understanding these differences is essential for caregivers and mental health professionals to provide effective support and interventions.
Community-based programs designed to combat depression among seniors can play a crucial role in safeguarding mental health. Such initiatives should focus on fostering social connections, providing mental health education, and encouraging peer support groups, which can mitigate feelings of loneliness and isolation. By prioritizing these factors, we can create a more inclusive community where older adults are equipped to manage their mental health.
Online Resources for Older Adults: Bridging the Gap
The rise of digital health platforms presents both challenges and opportunities for older adults seeking mental health resources. Online resources can provide valuable information on suicide prevention and mental health support; however, navigating these platforms often proves difficult for seniors due to technological barriers. Creating user-friendly websites and applications specifically designed for older adults can facilitate better access to critical mental health resources, thereby enhancing their ability to find help.
Moreover, ensuring that these online platforms contain tailored content aimed at elderly users can significantly improve engagement. Utilizing clear language and inclusive visuals, alongside contact information for local mental health services, can promote understanding and encourage individuals to reach out for support. This way, online resources for older adults can act as vital lifelines, connecting them with necessary help and reducing the stigma surrounding mental health access.
The Importance of Funding in Late-life Suicide Prevention
Inadequate funding for mental health initiatives targeting older adults presents a substantial barrier to effective suicide prevention. Research underscores that significantly more resources need to be allocated to understand and address the unique needs of older adults, and many funding bodies still prioritize younger demographics. To enact meaningful changes in late-life mental health support, advocacy for increased financial backing is essential.
With adequate funding, organizations can implement tailored suicide prevention programs that cater to the barriers faced by older individuals. This could include workshops for healthcare providers, enhanced outreach in communities, and the establishment of support networks that make it easier for older adults to access mental health resources and therapies aimed at reducing depression and suicidal ideation.
Creating Awareness through Public Campaigns
Public-facing campaigns are a critical component in raising awareness about suicide prevention among older adults. Efforts to educate communities and reduce stigma can empower older individuals to seek help while informing their families and caregivers about the signs of mental distress. Effective campaigns should focus on spreading knowledge surrounding the factors contributing to an increased risk of suicide in older populations, emphasizing the importance of mental health care.
Moreover, successful awareness initiatives can foster community involvement, encouraging individuals to participate in local outreach activities. By actively engaging seniors and their families, these campaigns can create supportive environments that promote dialogue about mental health and the resources available, which is vital for making any substantial changes in the statistics surrounding elder suicide.
Engaging Families in Elderly Suicide Prevention
Family plays a crucial role in the mental health of older adults, and engaging them in suicide prevention strategies is vital. Families often form the primary support system for elderly individuals, and equipping family members with the knowledge and tools to recognize warning signs can vastly improve the likelihood of timely intervention. Providing resources on geriatric suicide prevention to families can empower them to initiate meaningful conversations about mental health.
Support groups and educational workshops tailored for families of older adults can also be instrumental in fostering understanding and connection. By encouraging open discussions about depression and suicidal thoughts within families, we can dismantle stigma and create an atmosphere where older adults feel safe sharing their struggles. Increased family awareness can act as a buffer against isolation and enhance the protective factors essential in suicide prevention.
The Role of Technology in Promoting Mental Health
Advancements in technology can offer innovative solutions to mental health challenges faced by older adults. Utilizing telehealth services can significantly enhance access to mental health care, allowing elderly individuals to receive support from the comfort of their homes. These platforms facilitate consultations with mental health professionals while accommodating those with mobility issues and transportation difficulties.
Moreover, mental health apps that provide strategies for managing stress, anxiety, and depression are increasingly relevant. By incorporating these technological resources into geriatric care, we can create robust support systems that not only address immediate mental health needs but also promote ongoing wellness among older adults. As the digital landscape evolves, it is crucial to tailor these tools to make them accessible and engaging for older users.
Frequently Asked Questions
What mental health resources for seniors are available for suicide prevention?
Mental health resources for seniors, particularly for suicide prevention, include hotlines, counseling services, and support groups specifically designed for older adults. Organizations such as the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) and the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention provide targeted resources and information to help elderly individuals facing suicidal thoughts or depression.
How can geriatric suicide prevention be effectively promoted?
Geriatric suicide prevention can be effectively promoted through community outreach programs, public awareness campaigns, and the creation of tailored online resources. By addressing the unique needs of older adults, such initiatives can help reduce stigma and encourage seeking help, thereby improving overall mental health outcomes in this vulnerable population.
Why is elderly suicide awareness important in our communities?
Elderly suicide awareness is crucial because older adults are at a higher risk for suicide due to factors like isolation and mental health issues. Increased awareness can lead to better recognition of warning signs, prompt interventions, and ultimately save lives by connecting at-risk seniors with mental health resources.
What online resources for older adults can assist with suicide prevention?
Online resources for older adults include websites and platforms that offer mental health support, information on suicide risk, and connections to local services. Organizations like the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) and AARP provide access to materials that help educate seniors and their families about suicide prevention strategies.
How does depression in elderly communities relate to suicide prevention efforts?
Depression in elderly communities is a significant risk factor for suicide, making it essential to integrate mental health support into suicide prevention efforts. Recognizing the signs of depression and ensuring older adults have access to mental health resources enhances the effectiveness of suicide prevention initiatives tailored for this age group.
What strategies can be used to improve suicide prevention for older adults?
Strategies to improve suicide prevention for older adults include increasing access to mental health services tailored to their needs, raising awareness through educational campaigns, and fostering community support systems that help combat isolation and loneliness, both critical factors contributing to suicide risk.
How can family members support elderly suicide prevention efforts?
Family members can support elderly suicide prevention efforts by maintaining open lines of communication, encouraging regular mental health check-ups, being vigilant for signs of depression or suicidal thoughts, and actively involving their loved ones in social activities that reduce isolation.
What role do healthcare providers play in geriatric suicide prevention?
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in geriatric suicide prevention by screening older patients for depression and suicidal ideation, providing referrals to mental health services, and fostering a compassionate environment that encourages open discussions about mental health concerns.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| High Risk of Suicide | Older adults, especially those 75+, have the highest suicide rates of any age group. |
| Lack of Resources | Suicide prevention organizations do not provide sufficient resources targeted at older adults. |
| Study Findings | Research by McLean Hospital highlights the need for better suicide prevention strategies for older adults. |
| Online Information Scarcity | Older adults often find it difficult to locate relevant resources online. |
| Increasing Rates | Unlike younger age groups, suicide rates among those over 75 have been increasing. |
| Call for Action | There is a strong need for targeted public campaigns aimed at older adults and increased funding for research. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical issue, as this group experiences the highest rates of suicide yet lacks adequate resources for support. Research underscores the urgency of developing effective interventions tailored specifically for older individuals, addressing their unique healthcare needs and social challenges. By improving the accessibility of information and incorporating older adults in prevention efforts, we can significantly reduce the risk and provide much-needed help to this vulnerable population.